THE STRUCTURE AND LIFE PROCESSES OF AMOEBA PROTEUS
This blog post provides readers with the following objectives. The reader will be able to:
· Describe the structure of Amoeba
· Explain the life processes of Amoeba
{getToc} $title={Table of Contents} $count={Boolean} $expanded={Boolean}
Amoeba Definition and meaning
Habitat of Amoeba
Amoeba can be found in ponds, ditches, shallow muddy and in damp soils.
Structure of Amoeba
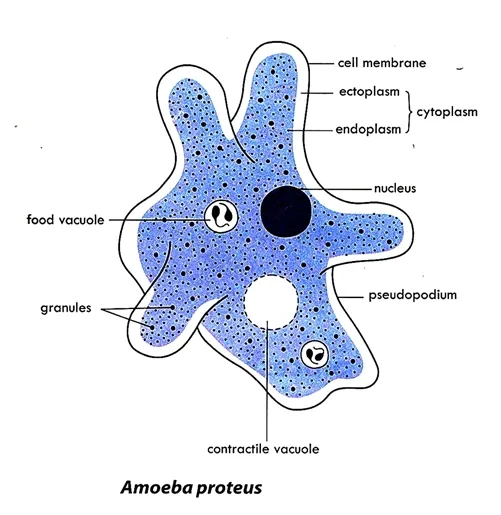
Amoeba is a unicellular organism. The body consists of protoplasm made up of the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The cytoplasm is made up of outer clear layer, called ectoplasm or plasmagel and more fluid, dense inner layer called endoplasm or plasmasol.
The endoplasm contains food vacuoles, contractile vacuoles and a dense nucleus. A food vacuole consists of partly digested food particles surrounded by bubbles of water.
A ‘false feet’ or pseudopodia projects from the body surface. Amoeba does not have constant shape. Its shape keeps changing by the formation of pseudopodia. It has a jelly-like body with no definite shape surrounded by a thin semi permeable membrane.
Diagram of Amoeba
Life Processes of Amoeba
Nutrition in Amoeba
What's the food for Amoeba?
Amoeba feeds on smaller organisms like bacteria, plankton and diatoms. It obtains its food through phagocytosis. It engulfs the food together with water with its pseudopodia to form food vacuole.
Enzymes are released from the cytoplasm into the food vacuole to digest the food. The soluble end product diffuses into the cytoplasm. The unwanted waste is released through the cell membrane by a process called exocytosis.
Irritability in Amoeba
Excretion in Amoeba
Waste products of metabolism in Amoeba include carbon dioxide, urea and ammonia. These waste products diffuse out through the cell membrane. Others are dissolved in water in contractile vacuole and they are eliminated together with excess water.
Respiration in Amoeba
Movement in Amoeba
Osmoregulation in Amoeba
Importance of osmoregulation
1. Osmoregulation enables Amoeba to maintain osmotic balance.
2. It also prevents Amoeba from bursting.
Reproduction in Amoeba
Binary Fission:
Amoeba reproduces asexually by binary fission. The process takes place in favorable condition. Amoeba stops moving and rounds off. The nucleus first constricts and divides followed by division of the cytoplasm. The daughter amoebae separate into two identical cells.Multiple Fission or Sporulation
Within the cyst the nucleus divides into many parts followed by division of the cytoplasm to form large numbers of amoebae. When conditions become favorable, the cyst break open and numerous amoebae come out in water.
Importance of Amoeba Proteus in Research
Amoeba Proteus is a model organism in scientific research due to its simple structure and the ease with which it can be observed under a microscope. Studies on amoebas contribute to our understanding of cell biology and the basic principles of life.
Conclusion
Amoeba Proteus, with its unique structure and efficient life processes, continues to captivate scientists and students alike. Its simplicity offers profound insights into the fundamental mechanisms of life.
Get Your Free PDF!
Download our comprehensive guide to
THE STRUCTURE AND LIFE PROCESSES OF AMOEBA PROTEUS
to boost your knowledge.
Download PDFClick the button above to get instant access to the PDF.



%20in%20Amoeba.webp)