MANAGEMENT IN LIVING: CONCEPT AND FOCUS (CONCISE NOTES FOR SHS)
By the end of this post, the readers should be able to:
· Explain the concept and focus of family life management.
· Outline the characteristics of management.
· Describe instances when management is needed.
· Outline the factors that affect management.
· Explain values and their roles in management.
· Classify values.
· Analyze the characteristics of values and their importance in Family Management.
· Classify goals with specific examples.
· Describe the guidelines for setting goals.
· Explain standards in management.
· Analyze the relationships between values, goals and standards.
· Differentiate between needs and wants.
· Analyze the effects of events on family life management.
Management
Management is an important discipline, and it exists
in almost every human activity be it school, bank, home, industry or
government. Management is the ability to accomplish goals or objectives through
efficient use of people and scarce resources. Everyone makes decisions in one
respect or the other and hence everybody could be regarded as a manager to some
extent. The student, the farmer, house wife, etc. are in one way or the other
engaged in managerial work.
In living, management is involved in every aspect of life; feeding the family, providing adequate clothing and shelter, adjusting to new situations, getting along with other people and family members, what equipment to buy, use of income (resources) are all matters of management. Management may therefore be defined as decisions and activities that make individuals or families get the kind of life they want through the use of the tools or the resources they have. OR
Management is making use of available resources to
achieve goals or meet needs and wants of the family.
Home management involves using resources available to individuals and families in the home to achieve the quality of life the family wants.
For more details on management principles, visit Mind Tools.
Focus of Management
Management involves:
(i) Identifying needs and wants.
(ii) Using resources at one's disposal judiciously.
(iii) Various activities i.e., planning, implementing and evaluating actions.
(iv) Involves decision making.
It is therefore the process of using the family's resources to meet the family's needs or goals. It requires mental work and the physical power of family members. Good management of family resources leads to improvement in the quality of living within the family and happiness in the home. For more on management practices, check out this resource on management fundamentals.
Characteristics of Management Situations
All management situations have some characteristics in
common;
(i) An individual or group have the idea of what is
needed.
(ii) Someone must or should judge or assess what is
available for use in terms of tools or resources.
(iii) Someone reconciles differences between what is
needed, wanted and what is available.
(iv) Someone needs to know what is likely to happen
under certain circumstances.
(v) Someone recognizes the limitations of what can be
done as against what is available.
(vi) Someone brings together what is needed at the
right time — tools, materials, ingredients to identify the place and activities
that will take place and the people to carry out the activities.
Instances When Management Is Needed
Management is needed when;
(i) There is a problem to be solved.
(ii) The resources we have are limited or inadequate
in relation to our needs/wants.
(iii) Using the same resources for many things.
(iv) We are not achieving our goals.
(v) There is conflict of wants/needs.
(vi) There is the need for change.
A Manager
A manager is a person who takes responsibility for decisions about goals and the use of resources. He is therefore a person who plans, organizes, directs, controls and coordinates activities in order to guide an organization towards the achievement of its stated objectives and goals. He is responsible for directing the efforts aimed at helping the organization achieve its goals.
Qualities of a Manager
Characteristics
of a good manager include the following:
- Visionary: Ability to foresee future needs and plan accordingly, such as setting goals for short-term and long-term achievements.
- Resource Identification: Recognizing necessary resources to achieve objectives, e.g., selecting a university, acquiring books, and securing accommodation for a degree.
- Implementation: Ensuring plans are executed, such as creating a private study timetable for academic success.
- Considerate: Being friendly, impartial, and sensitive to the needs of family members.
- Integrity: Being honest, sincere, trustworthy, and faithful.
For more information, visit this management guide.
Factors that Affect Management
(i) Age of Person: Age influences the level of maturity and experience of the person. An adult is more experienced and likely to manage better than an adolescent.
(ii) Knowledge: Knowledge about resources and how to manage as well as the ability to apply information contribute to success of management.
(iii) Health: The health of the individual contributes to the capacity to work and put plans into action.
(iv) Experiences: The more experienced a person, the better he is able to plan and implement plans with minimum errors.
(v) Resources: Material and human resources available affect the success of management.
(vi) Values and goals
(vii)
Needs and wants: These motivate individuals and families to take action.
Motivators of Management
(i) Values
They are the beliefs,
feelings and experiences that people consider important and desirable. They are
things that we consider very desirable, important, or worth doing. It explains
why people do things.
Values
cannot be seen. These partly explains why individuals do certain things and
avoid others. Values influence the choice you make among alternatives. E.g., A
family or individual for whom education is important will spend more time and
money on education. Examples of values are freedom, privacy, beauty, comfort,
peace, knowledge, wealth, security, love, honesty and achievement. Each family
needs to work out its own set of values which are suitable and agreeable to its
entire members.
Importance of Values
(i)
Values influence our behaviors, decisions and choices. They give meaning to our
lives and determine the type of goals and objectives we set for ourselves and
family.
(ii)
Values influence the way we manage our families in terms of the choice and use
of scarce resources.
(iii)
Values of a family will help them determine what they consider as needs and
what they consider as wants. This will help them set their goals and determine
how to use resources to achieve these goals.
(iv)
Values help determine what we are prepared to work for.
(v)
Values help us to select from the many alternatives or choices the one that
will help us achieve our goals or objectives.
(vi) Our values help us to set standards for ourselves and families.
Sources of Values
Values
develop from:
(i)
Personal experiences as basic needs are met.
(ii)
Family influences.
(iii)
The culture in which you live. (iv) Peer influences.
(v)
Daily activities and the people we interact with.
Classification of Values
Values
can be classified in different ways. For our purpose we are classifying values
as follows:
a) Personal Values
These
are values that are important to individuals e.g.
(i)
Punctuality
(ii)
Devotion to work
(iii)
Independence
(iv) Beauty
These
may differ for individuals within the family and may affect family decisions.
b) Mora/ Values
These
indicate what is wrong or right behaviors e.g.
(i)
Honesty
(ii)
Integrity
(iii)
Trustworthiness
(iv)
Dependability
(v)
Truthfulness
c)
Social Values
Social
Values are those which deal with relationships with others since human beings
are not alone. E.g.
(i) Tolerance
(ii) Co-operation
(iii) Kindness
(iv) Acceptance
(v) Friendship
These
values relate to commitments to the home, the family and the community.
d) Societal Values
These
are values held by a nation, a community or a group within the society. They
may be generally accepted beliefs related to the culture of the people. E.g.
(i) Women in the society
(ii) Dressing
(iii) Code of behavior
(iv) Respect for the elderly
Values
which are widely held are very powerful and very difficult to contradict.
e) Intrinsic Values
These
are values that are good and important for their own sake. They are the higher
values such as love, aesthetic, freedom, truth, etc.
f) Instrumental or Extrinsic Values
These
are values which we seek as way of achieving higher values. E.g., Orderliness
in a house is a value which can be used to achieve a higher value like
aesthetics in a home. Values such as comfort, health,
knowledge
or religion can be both intrinsic and instrumental.
Note:
Although values cannot be seen, they influence behaviors, decisions and choices
consciously or unconsciously. Values influence family management in terms of
resource choice and use, goals and standards
set.
Characteristics
of Values
(i)
Values are abstract not concrete.
(ii)
They are complex, i.e., sometimes one does not know which value is operating.
(iii)
They are expressed in strong terms, i.e., they involve emotions.
(iv)
Values change in importance overtime.
e.g.,
value can change over the family life cycle or with different experiences.
(ii) Goals
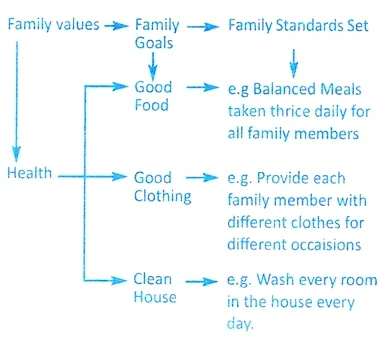
Goals are targets you set for yourself or what you aim to accomplish. Goals are things you intend to do or things you want to get done or achieve. Goals are aims, ends or things individuals and families work to achieve. Goals give direction. Like values, goals change overtime and they are ends in view. Our goals are closely related to our values. We decide what we want because of our values. Our goals therefore reflect our values.
Classification/Types of Goals
i).
Long term goals
These are goals that take relatively long periods of time to achieve. They represent the conditions you are trying to obtain in the future. They are sought over long periods of time. E.g., the family wants to build a house, start a farm or business, buy a car, save for retirement, etc. These are long term goals. They are goals which are normally considered to be fairly permanent and set to be achieved in the distant future.
ii)
Short term goals
These
are goals that can be accomplished in a relatively short time. They may take
days, weeks, months or a year to accomplish. E.g., Passing your exams, getting
a dress made, learning how to play an organ.
iii)
Inter-mediate goals
They
take longer time to accomplish. Long term goals are achieved through
intermediate goals. They therefore serve as a means of achieving long term
goals and are normally more definite or specific than long term goals. E.g.,
saving towards building a
house,
passing your exams to gain admission to a tertiary institution and getting a
traveling passport.
iv)
Means - end goals
They
are simple and immediate goals set up as steps to achieve other goals.
Means-end goals are the day-to-day decisions and activities taken towards the
attainment of goals. E.g., in order to pass your examination, you attend
lectures, study hard and do your homework.
Guidelines for setting goals
(i) Start by making a list of what you want
in life.
(ii) Consider your values (since values shape
goals).
(iii) Arrange
what you want in order of importance.
(iv) Set long term goals before short term and
instrumental goals.
(v) Goals should be precise, clear and
realistic, measurable or quantifiable and time bound.
(iii) STANDARDS
We
set standards in our daily lives whether we are individuals or we are in a
family. They are what a person or family will accept as good and worthwhile.
Standards are a set of criteria for measuring goal attainment. They therefore measure how well we want to achieve any purpose or goals in management. They also determine the type of resource that we will use. They are used to measure the value of something such as an activity and the satisfaction received from such an activity.
(i) Standards serve as a measure of quality, quantity as well as the degree of accomplishment that we would find acceptable or adequate.
(ii)
Standards develop from our values and therefore originate from the society in
which we live.
(iii) Standards are used to measure the value of something, such as activity e.g. standard of living and the satisfaction received from such an activity.
iv)
The standards set by a family influence or determine their use of resources.
E.g. providing three 3 meals a day can be the goal of a family but the standard
could be that the meals must be balanced and served on the dining table.
Classification
of Standards
Standards
can be classified into two main groups
(i) Quantitative/Objective Standards
(ii) Qualitative/Subjective Standards
Quantitative/Objective Standards
They
are measures that give precise amounts of what is desired. They are the easiest
standards to identify because they can be seen and are related to quantities
such as weight, lengths, and requirements to pass examinations.
Qualitative/Subjective Standards
They
measure quality. They are based on personal opinions. As such, individuals have
different criteria for measuring what is "good" or "bad".
Thus, what may be viewed as "good" by one person may be viewed as
"bad" by another. They are not easily identifiable with specific measures
such as taste, texture or beauty.
Note:
Some subjective standards are referred to as conventional or rigid standards.
They are often related to traditions, social customs and social behaviors.
Non-Conventional
standards: Tend to be flexible. These standards may be set to suit
available resources or situations.
RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN VALUES, GOALS AND STANDARDS
Values,
goals and standards are related:
(i)
Values are primary reasons for our actions and decisions. They are the reasons
why we do the things we do.
(ii)
Goals are set based on our values as the objectives we want to achieve or what
we want to be.
(iii) Standards are set to measure goal attainment. The standards show how well we have achieved our goals based on our values.
(iv) Standards set in family management, are also based on values.
For further insights, explore Values, Goals, and Standards.
NEEDS AND WANTS
Needs: Are things we cannot do without. They are basic items you must have to live as a human being e.g. food, shelter, clothing, etc. A need can be explained as the gap or difference between where we are or what we have and where we want to be or what we want. E.g. a hungry or sick man is in a state of need. He wants food or good health. Needs must be met for your growth and development.
Wants: Are things that
we can do without but would like to have in order to enhance the quality of
life e.g. a mobile phone, a car, etc. In short, wants are what you desire.
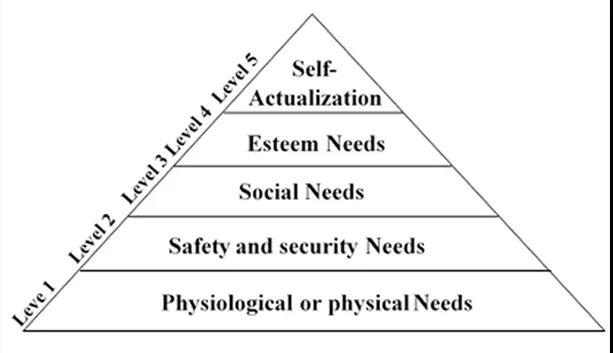
Levels of Needs
There are different levels of needs. They can be
placed in a hierarchical order. People tend to satisfy lower-level needs before
high level ones.
Physiological Needs
These are the lowest level of needs; these are
important in maintaining life and are therefore essential for the survival of
human beings e.g., food, clothing, shelter and elimination of waste.
Safety Needs
These include freedom from fear, threat, danger of
being in deprivation.
Social Needs
They relate to social interaction. We attain them only
when we love and are loved make one feels a sense of belonging.
Esteem Needs
Include the need to be respected and recognized by
people or society. When people have achieved the other lower needs, they want
to be recognized in society in life.
Self-Actualization Needs
These are the highest level of needs. It is the level
at which individuals realize their full potential and capabilities.
EVENTS
Events are unexpected or unforeseen, or unanticipated occurrences or incidents that are outside the control of the individual and the family such as sudden illness, fire outbreak, accident, unexpected guest, burglary, death, etc.
Events are not usually planned for but they require attention when they occur. They may require the changing of plans, use of resources, and making of new decisions. Events require careful management to enable families and individuals to meet them.
Effects of Events on Family Life Management
Since events require immediate response or acting, they motivate us to manage when they occur. E.g., when you receive an unexpected visitor, you have to find the resources to feed and accommodate him/her. Events therefore, urge us to make new decisions and plans.
Even though it is very difficult to predict the occurrence of events, preventive measures can be taken or put in place to minimize its effects should they occur.
Management in living WASSCE Questions and Answers
1.(a). What are values? (June 2001)
Values are things we consider very desirable, important or worth doing. They are what we prize or cherish in life or the beliefs, feelings and experiences that people consider to be important and desirable.
(b). In what ways can values affect your goals?
The ways in which values can affect your goals include:
i. Values help us set standards.
ii. Values help us determine how to use our resources to achieve our goals.
iii. Values determine the types of goals we set.
iv. Valves help us in selecting from the many alternatives to achieve a goal.
v. Our values also determine the way of doing things or methodology.
(c) State short-term goals that can help a person accomplish a long-term goal of building a house
(i) Save enough money.
(ii) Acquire or buy a plot of land.
(iii) Make a building plan.
(iv) Get the services of a contractor or architect.
(v) Buy building materials.
(vi) Make the foundation.
(vii) Get the building to the lintel and roofing levels.
(viii) Fix the roof.
(ix) Plaster the structure.
(x) Provide fixtures and fittings.
(xi) Paint the building.
2.a. State three characteristics of a good home manager. (June 2003)
i) She must be responsible.
ii) She must be critical and have a good sense of judgment.
iii) She must be creative, resourceful and can use her initiative.
She must have foresight and intelligence.
(b). Explain each of the characteristics mentioned in 2(a) above and give an example of each.
(i) A good home manager who is responsible is trustworthy, and reliable, and is able to use the resources available to the family for a purpose or to achieve specific family goals. E.g., she is responsible for all decisions with regards to goods and services which the family use e.g., food, clothing, water etc.
A good home manager who is critical and have a good sense of judgment is able to implement and control activities and therefore ensures that plans are carried out successfully.
iii) Being creative, resourceful and able to use her initiative means that she should be able to use the limited family resource (money) judiciously e.g., instead of buying new items, she goes in for second hand items.
iv) A good home manager must have foresight and be intelligent. This means that she should be able to look into the future e.g., buy foodstuffs, cereals during the harvesting period.
3. a. i. What is management? (June 2006)
Management is making use of available resources to achieve goals or meet needs and wants of the family. It is therefore the process of making use of what you have to achieve what you want
ii. Explain four steps in the management process
(a) Planning: Planning involves identifying needs or setting goals and showing how to use the resources available to achieve them.
(b) Organizing: It is concerned with the arrangement of the activities to be performed in the plan in a logical sequence / logical manner.
(c) Implementation: This involves the actual process of putting the plan into action
(d) Evaluation: This involves looking back or assessing to determine how far goals have been achieved and for future actions
4.a. Explain how any two of the following personal characteristics affect management:
(i) Age
(ii) Knowledge
(iii) Experience (June 2008)
(i) Age of person: Age influences the level of maturity and experience of the person. An adult is more experienced and likely to manage better than an adolescent.
(ii) Knowledge: Knowledge about resources and how to manage as well as the ability to apply information contribute to the success of management. For example, in this present era technological and social changes have given rise to conflict as individuals and families are faced with many choices every day.
(iii) Experience: Experience influences the way people formulate plans. The more experienced a person, is the better he is able to plan and implement plans with minimal errors and efforts.
(b). Define values and state how they affect behavior
Values are what a person prices or cherishes in life. They are the beliefs, feelings and experiences that people consider to be important and desirable. Values motivate us to behave or act the way we do and influence our interaction with others. Values therefore influences behavior and decisions and choices consciously or unconsciously. They determine the kind of life, desired goals and standards set and resources to be used.
5.a. What are motivators in management? (June 2009)
Motivators are things that influence or push people to manage or use resources the way they do.
b. Explain five motivators that influence the management process
(i) Values: They are the beliefs, feelings and experiences that people consider important and desirable.(ii) Goals: Goals are targets you set for yourself OR what you aim to accomplish or things you want to get done or achieved.
(iii) Standards: Standards serve as a measure of the level to which people want to achieve goals
(iv) Needs: These are things we cannot do without e.g., food and clothing
(v) Wants: These are things we can do without but would like to have in order to enhance the quality of life e.g., a car, a mobile phone, etc.
(vi) Events: These are things outside your control, they are unexpected occurrences. E.g., sudden illness, accident, fire outbreak, etc.
c. State two reasons why resources must be managed
(i) Individual or family needs and wants are many while resources are limited or scarce. Therefore, there is the need to manage the limited resources that are available effectively and efficiently.
(ii) Resources must be managed so that the individual or family may be able to control or handle events of life when they occur
(iii) Resources are managed so that they could be used in an organized way or manner
(iv) Resources are managed so that they could be developed, transported or saved for future use.
d. State two situations that require the management of resources
(i) When there is shortage of resources or when resources are limited or scarce.
(ii) When there are many goals, needs, wants and emergencies to meet.
(iii) When there is (are) problem(s) to solve
6. Explain the following pairs of words to bring out their differences in meaning (1993)
(i) Values and goals: Values are things that we consider very desirable, important and worth doing. It explains why people do things while goals are targets you set for yourself. That is what you aim to accomplish. Values thus help individuals to set goals or objectives or aims in their lives.
(ii) Needs and wants: Needs are important things we cannot do without. They are basic items you must have to live as a human being e.g., food, shelter, clothing etc. but wants are things that we can do without but would like to have in order to enhance the quality of life e.g., a mobile phone, a car, etc.
(iii) Human and non-human resources: Human resources are human characteristics that individuals possess and can be used to achieve goals e.g., knowledge, skills, mental health, energy, time etc., whilst non-human resources are material possessions that people have and can be used to achieve goals e.g., money, equipment, furniture, houses etc.
(iv) Planning and evaluation: Planning involves setting goals and goal clarification, identifying resources to be used, setting standards and organizing to achieve the set goals. Whilst evaluation is the last step in the management process and involves looking back or assessing to determine how far goals have been achieved and for future action.
7.Why would you say that values, goals and needs are interrelated? Illustrate your answer with specific examples
Values, goals and needs affect and are related to each other. The goals we set depends on our values. Values help individuals and families to distinguish between needs and wants and to decide the kind of resources to use. If your value is education or knowledge, your goal will be to study hard to pass your examinations well. This determines your needs which include getting a school, books, fees etc.
Therefore, your values will help you differentiate what is necessary (your needs) from your want. This will in turn help you to set goals and determine how to use available resources to achieve these goals.
8.a) What is a realistic goal?
A realistic goal is an achievable goal. A goal that one can possibly be achieved or attained
(b) State four reasons for setting realistic goals
(i) Realistic goals help individuals to be successful
(ii) They help prevent frustration and disappointments
(iii) Realistic goals prevent wastage of resources
(iv) They give a feeling of satisfaction when goals are achieved or attained
(v) When set goals are attained, it urges people on to desire to achieve more
9.(a) Identify one long term goal which is related to one's education
(i) Go to the university or the Polytechnic or training college
(ii) Study home economics, business, science or arts
(iii) Passing WASSCE
(iv) Career or job
(b) Explain any two factors that can cause a change in family goals
(i) Events: They are unexpected occurrences and may require the changing of plans or family goals, use of resources and making new decisions
(ii) Change in family values: Goals depend on values, thus a sudden change in family values can cause a change in family goals
(iii) Stages of the family lifecycle: Different stages of the family life cycle have different demands or needs or works which may cause a change in family goals.
(iv) Inadequate or limited resources: When resources (money) are inadequate or not enough to meet family needs, it can cause a change in family goals.
EXAMINATION QUESTIONS
l. a. Who is a good manager?
b. State FOUR characteristics of management.
c. Outline FOUR things or activities involved in good management
d. Give two reasons why it may not be easy to achieve good management in a family (November 2006)
2. a. State two reasons why one needs to manage every situation in life.
b. Describe three characteristics of management
c. Describe two qualities of a good manager
d. Explain three importance of evaluation in management (November 2009)
3. a. Explain the following concepts
(i) Values
(ii) Needs
(iv) Wants
b. Explain the relationship between the concept listed in (a) above
c. Kofi's values are knowledge and good health. Set two goals each to show how Kofi will realize these values.
4. State the difference between a long-term goal and a short-term goal.
a. What is management?
b. State five characteristics of management.
5. Explain the following concepts
(i) Intermediate goals
(ii) Short term goals
b. State FIVE guidelines for setting goals.
6. a. Explain the concept standard.
b. Distinguish between quantitative standards and qualitative standards.
7. a. What is a realistic goal?
b. State four reasons for setting realistic goals.
c. Building a house is a long-term goal. State eight short term goals that would help achieve this goal (June 2009)
8. a. Why is decision making important in management? (Nov 1995)
b. List the steps in the management process.
9. a. Why would you say that values, goals and needs are interrelated? Illustrate your answer with specific examples (Nov 1996).
10. Identify and explain four characteristics of a person who is considered a good manager.
Give one specific example of each characteristic (Nov 1996)
11. a. Outline three (3) main steps in the management process (Nov 1997)
b. Describe four activities or decisions that occur in the first stage of the process